|
Medical Advocates for Social Justice
Conference Poster
|
 |
1st International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Pathogenesis and Treatment.
Buenos Aires,
Argentina -
July 8 - July 11, 2001
Safety of Kaletra: Data from Phase II and Phase III Clinical Trials.
B Bernstein, M King, S Brun, P Cernohous, A
Potthoff, J Moseley, M Sullivan, K Grebner, and E Sun.
Abbott Laboratories, Antiviral Venture, Abbott Park, IL USA
|
|
BACKGROUND
Lopinavir is an HIV protease inhibitor (PI) that is co-formulated with ritonavir, an inhibitor of cytochrome P450-3A, as Kaletra. The standard dose of Kaletra is
400 mgLPV/100 mg ritonavir, as 3 co-formulated capsules, BID. Kaletra has been studied in clinical trials in over 500 patients ranging from antiretroviral (ARV) naïve
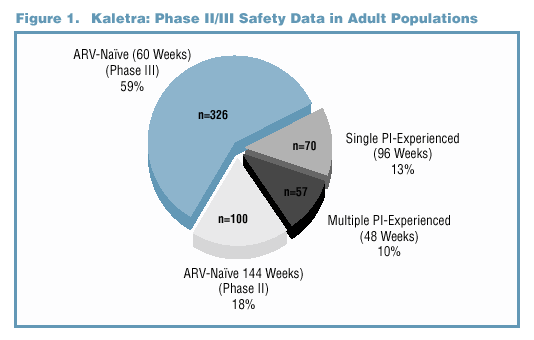
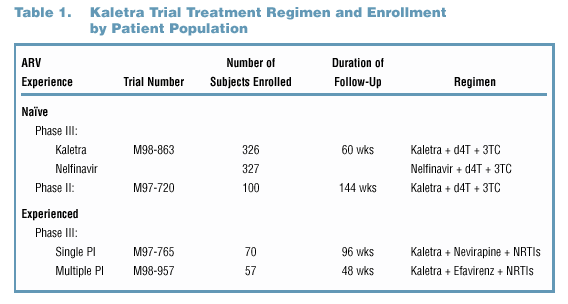
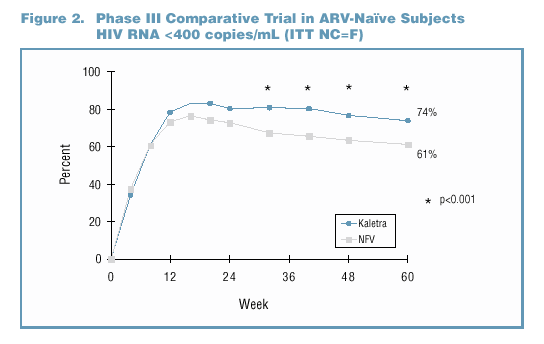
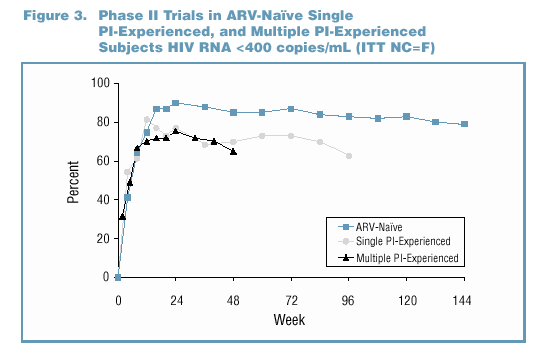
to multiple PI experienced (Figure 1 and Table 1). Superior efficacy has been demonstrated with data from Study M98-863, a Phase III comparative trial of ARV-naïve
patients comparing Kaletra (n=326) to nelfinavir (n=327) (Figure 2). In Phase II trials, antiviral activity has been demonstrated in ARV-naïve patients (Study M97-720,
n=100), in single PI-experienced patients (Study M97-765, n=70), and in multiple PI-experienced patients (Study M98-957, n=57) (Figure 3).
METHODS
The safety and tolerability of Kaletra were examined in Phase II and III clinical
trials through collection of adverse events (AEs) with severity/relationship
assessed by investigator. Laboratory tests were conducted without regard to
fasting. Results are expressed as the cumulative incidence over the durations
noted.
RESULTS
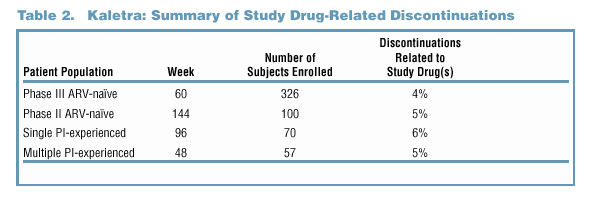
Study Drug-Related Discontinuations
-
Study drug-related discontinuations were infrequent in Phase II/III clinical trials, reflecting the overall tolerability of Kaletra (Table 2).
Adverse Events
- Adverse events of at
least moderate severity and possible, probable, or unknown relationship to
study medication as determined by the investigator are summarized in Tables
3 and 4. Moderate is defined as "causing discomfort and interrupting the subject's
normal activity."
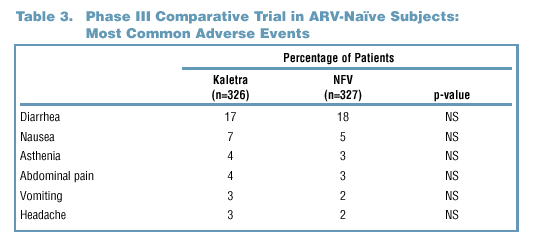
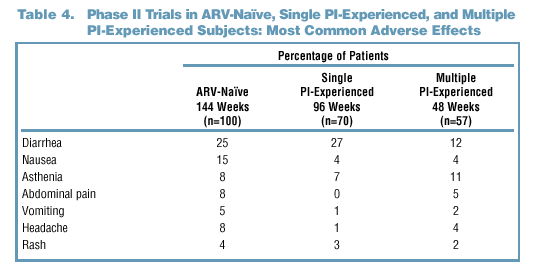
- Gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms (diarrhea and nausea) were the most common
AEs observed in both Phase II and Phase III clinical trials. These occurred
with similar frequency in the Kaletra and nelfinavir arms of the Phase
III trial.
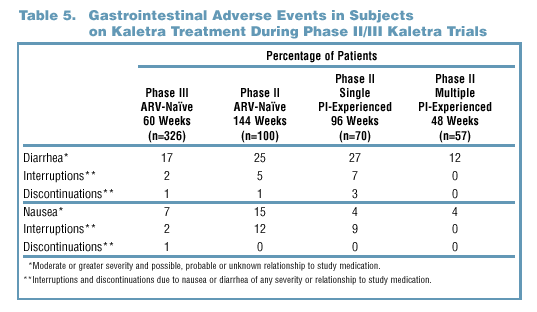
- In both Phase II and Phase III trials, study drug discontinuations and
interruptions due to GI AEs were infrequent (Table 5).
- The higher rates of GI AEs seen in some Phase II trials may reflect
the use of doses of LPV/r greater than 400 mg/100 mg in some patients
as well as the longer duration of follow-up.
Laboratory Abnormalities
-
In general, laboratory determinations were obtained monthly for the
first six months of the trials, then every two months through Week 48,
and quarterly thereafter.
-
Laboratory determinations were performed without regard to fasting.
-
Severity grades based on the Division of AIDS Grading Severity of
Adult Adverse Events criteria.
- The most common laboratory
abnormalities observed in Phase III were elevations in triglycerides and
total cholesterol.
Laboratory Abnormalities Observed in the Phase III Trial Through
Week 60
- Hyperlipidemia-Triglycerides
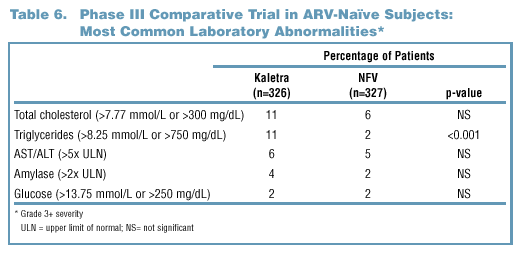
- Elevations of triglycerides were reported more commonly in Kaletra
than nelfinavir treated patients (11% vs. 2%, see Table 6).
- The maximum triglyceride level experienced by the majority of
patients in both treatment groups was <400 mg/dL (Figure 4).
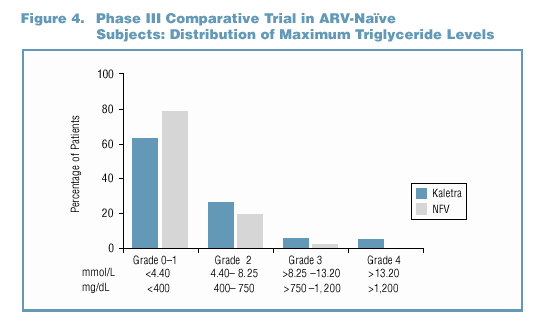
- Hyperlipidemia-Cholesterol
- The maximum cholesterol level experienced by the majority of
patients in both treatment groups was < 240 mg/dL (Figure 5).
- Hyperlipidemia-Intermittency
- Participants
had an average of 7 laboratory determinations performed during
the study obtained without regard to fasting. In participants
with Grade 3/4 triglyceride or cholesterol elevations, the abnormality
was generally intermittent, with most having only 1-2 measurements
reach this magnitude.
- Grade 3/4 triglyceride elevations were not associated with pancreatitis.
- Lipid Subfraction
Determination
-
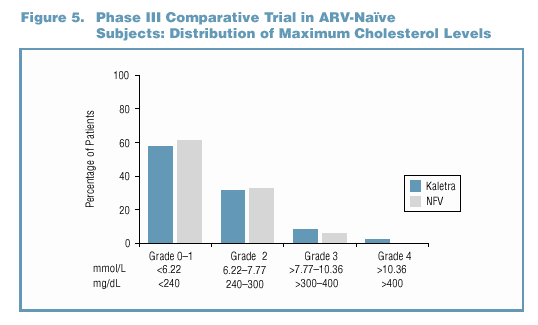
Both total cholesterol (TC) and high density lipoprotein
(HDL) cholesterol rose between baseline and Week 24 in Phase
III subjects receiving Kaletra or nelfinavir therapy (Figure
6). Measurements were performed on these patients who were
fasting at both baseline and Week 24. The change in the
TC/HDL ratio was not statistically significant (p=0.179)
in subjects treated with Kaletra. A small, but statistically
significant (p<0.001) increase in the ratio was observed
in nelfinavir-treated patients.
Laboratory Abnormalities Observed in Other Clinical Trials
- Lipid elevations, when present, tended to occur early
and were generally non-progressive over time (Figure 7 and
Figure 8).
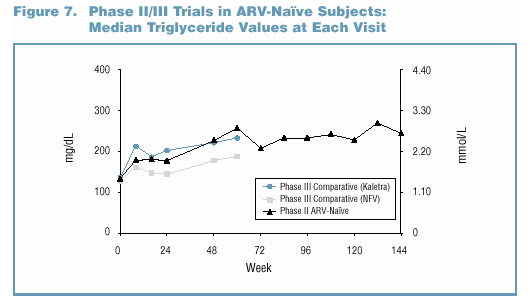
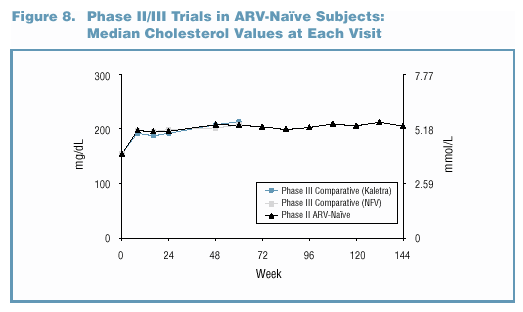
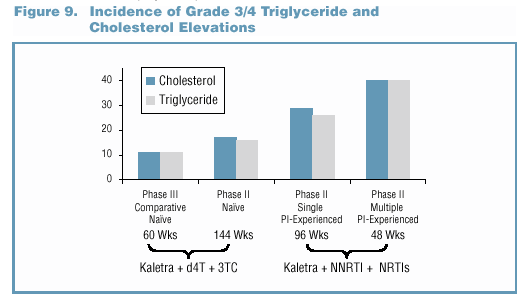
- In the Phase II/III trials, no patient discontinued due
to study drug-related Grade 3/4 lipid elevations. o Grade
3/4 lipid elevations occurred more frequently in Kaletra trials
involving PI-experienced patients (Figure 9).
- A multivariate
analysis was performed across all trials through Week 48 to
identify the potential risk factors for Grade 3/4 triglyceride
and/or cholesterol elevations.
- Risk factors for Grade 3/4 triglyceride elevations were
found to be:
- Elevated baseline triglycerides
- Prior PI/current NNRTI use
- Risk factors for Grade 3/4 cholesterol elevations were
found to be:
- Elevated baseline cholesterol
- Prior zidovudine (AZT) and PI use
- >1 year since HIV diagnosis
- Hepatitis C negative
- Treatment for lipid elevations was left to the discretion
of the investigator with basic management guidelines discussed
in the clinical protocols. Less than half the patients who
experienced a Grade 3/4 lipid elevation received pharmacologic
therapy for hyperlipidemia. When prescribed, treatment with
pharmacologic lipid-lowering agents resulted in a median
decrease in cholesterol values of 17% and a median decrease
in triglyceride values of 48%.
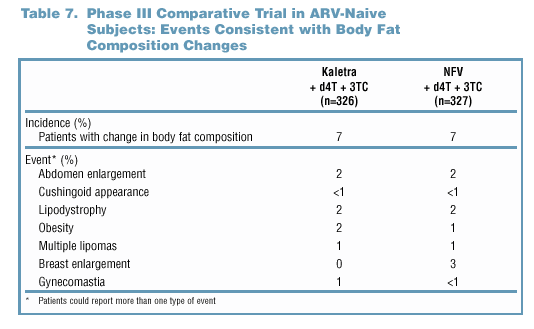
Treatment-Emergent Body Fat Composition Changes
- Investigators were instructed to report as AEs all episodes
of central adiposity, peripheral fat wasting, breast hypertrophy,
dorsal fat pad, multiple lipomas, and Cushingoid appearance.
Also considered as body fat composition changes were episodes
of abdomen enlargement, obesity, lipodystrophy, breast enlargement,
and gynecomastia.
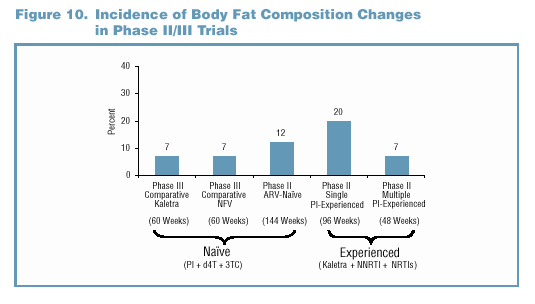
- Through 60 weeks of treatment, AEs consistent with body
composition changes were noted in 7% of patients in either
treatment arm in the Phase III comparative trial (Table
7). There was no association between these events and Grade
3/4 lipid elevations.
- The incidence of body fat composition changes across all
Kaletra trials is presented in Figure 10.
Safety in Patients with Hepatitis B or C in the Phase
III Comparative Trial
In the Phase III comparative trial, 115 patients who were
hepatitis B surface antigen positive (n=39) or hepatitis
C antibody positive (n=76) at baseline had on-study laboratory
determinations performed.
Patients were allowed to participate in the Phase III
comparative trial if their screening LFTs were <3x ULN.
Patients were allowed to remain on medication unless their
LFTs exceeded 10x ULN, provided they remained asymptomatic
without concomitant Grade 3+ elevations in total bilirubin
or alkaline phosphatase. The incidence of Grade 3+ AST/ALT
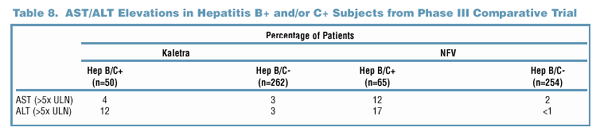
elevations is summarized in Table 8.
 Kaletra has been well tolerated in Phase II/III trials
as reflected by the low rates of study drug-related discontinuations
observed.
Kaletra has been well tolerated in Phase II/III trials
as reflected by the low rates of study drug-related discontinuations
observed.
In both Phase II and Phase III trials, the most common
AEs were gastrointestinal in origin and infrequently resulted
in study discontinuation or interruption.
Lipid elevations were the most commonly observed laboratory
abnormalities observed in the Phase II and Phase III trials
and occurred more often in patients with prior PI-experience
and higher baseline lipid levels. Study discontinuations
or interruptions due to elevated lipids were infrequent.
Elevated lipid levels were generally intermittent and responded
to lipid lowering agents.
CONCLUSIONS
- Risk of Grade 3/4 AST/ALT elevations was greater in hepatitis
B/C+ patients compared to hepatitis B/C-. Risks of elevation
were comparable between hepatitis B+ and hepatitis C+ patients.The
relative risk (95% CI) of Grade 3/4 elevations based on
hepatitis status was 3.3 (1.4, 8.2) for the Kaletra group
and 10.2 (3.8, 27.5) for the nelfinavir group.
- Within each treatment group, the mean change in AST/ALT
from baseline was similar regardless of hepatitis status.
- Four study drug interruptions occurred as a result of
Grade 3/4 AST/ALT elevations (1 Kaletra patient, 3 NFV patients).
No hepatitis B/C+ patient discontinued the study due to
Grade 3/4 LFTs.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The subjects, investigators, and coordinators from studies
M97-720, M97-765, M98-863, and M98-957
TOP

Poster
Safety
of Kaletra: Data from Phase II and Phase III Clinical Trials
© 2001
Medical Advocates for Social Justice
Email: info@medadvocates.org

















